The journey of musical instruments is a fascinating tale that spans centuries, reflecting the cultural, technological, and artistic developments of human civilization. From the primitive sounds produced by early humans using rudimentary tools to the sophisticated electronic devices of today, the evolution of musical instruments has been marked by innovation and creativity. Early instruments, such as flutes made from bones and drums crafted from animal skins, laid the groundwork for more complex creations.
As societies advanced, so did their musical expressions, leading to the development of stringed instruments like the lyre and lute, which became central to various cultural traditions. With the advent of the Industrial Revolution, the manufacturing of musical instruments underwent a significant transformation. The introduction of new materials and production techniques allowed for greater precision and consistency in instrument design.
This period saw the birth of iconic instruments such as the piano and the saxophone, which not only enriched musical genres but also expanded the possibilities for composers and performers. As technology continued to evolve, so did the instruments themselves, leading to the emergence of electric guitars and synthesizers in the 20th century. These innovations not only changed how music was created but also how it was consumed, paving the way for new genres and styles that would dominate the music landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Musical instruments have evolved over time, from simple tools to complex, technologically advanced devices.
- Augmented instruments are traditional instruments that have been enhanced with technology to expand their capabilities and create new sounds.
- Augmented instruments are revolutionizing the music industry by offering musicians new creative possibilities and enhancing live performances.
- Technology has had a significant impact on music creation, allowing artists to experiment with new sounds and production techniques.
- Augmented reality is playing a significant role in music by providing immersive and interactive experiences for both musicians and audiences.
What are Augmented Instruments?
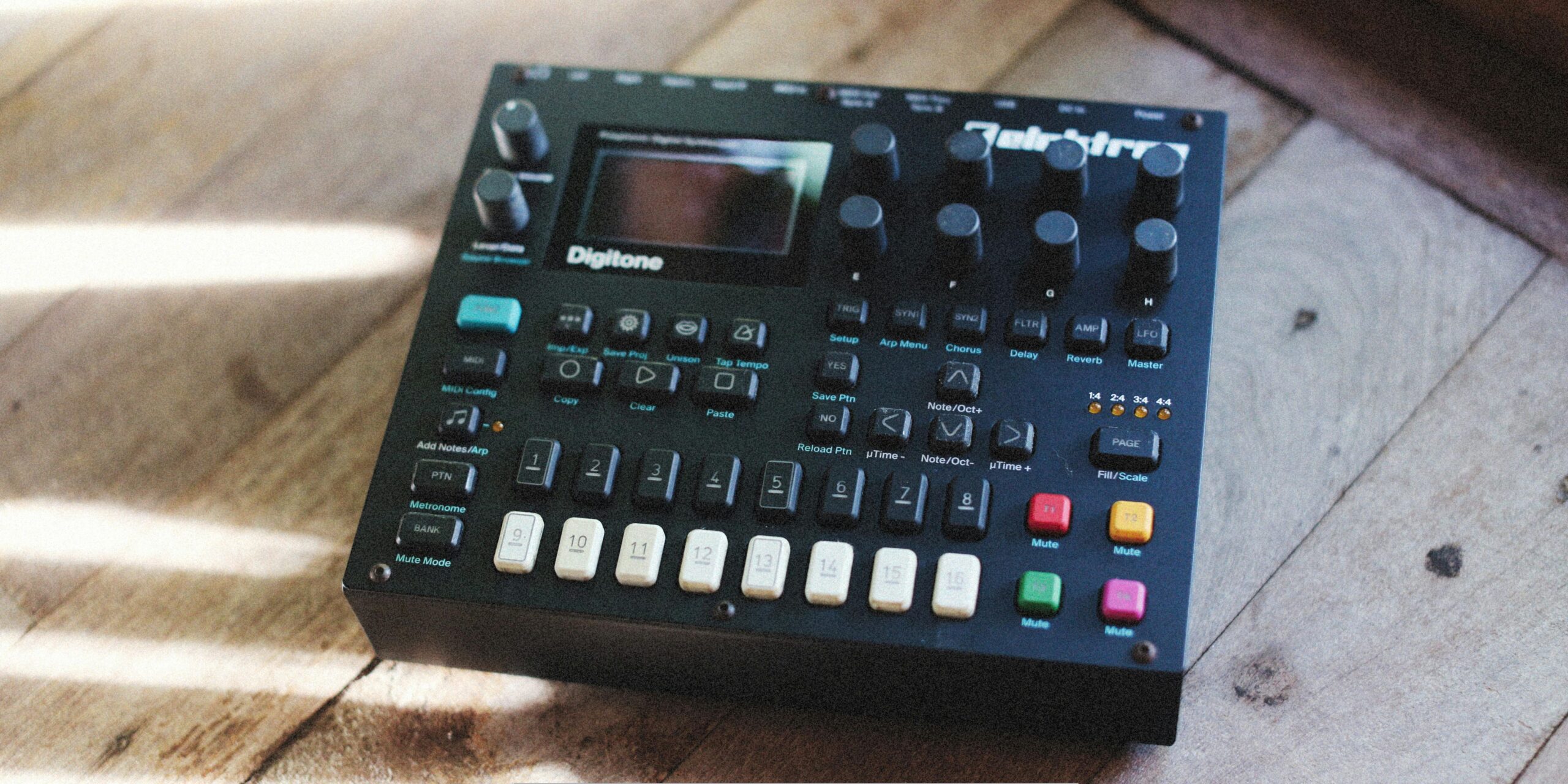
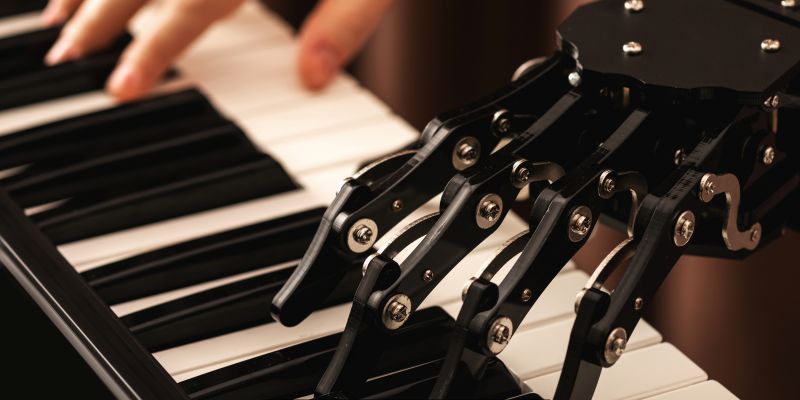
Augmented instruments represent a groundbreaking fusion of traditional musical craftsmanship and modern technology. These instruments are enhanced with digital components that allow for a broader range of sounds and interactive capabilities. Unlike conventional instruments, which produce sound solely through physical means, augmented instruments utilize sensors, software, and other technological enhancements to expand their functionality.
This integration enables musicians to manipulate sound in real-time, creating a dynamic performance experience that was previously unattainable. The concept of augmented instruments encompasses a wide array of devices, from digitally modified violins to electronic drum kits that respond to touch and movement. These instruments often come equipped with features such as MIDI compatibility, allowing them to interface with computers and software for recording and production purposes.
The result is a new realm of possibilities for musicians, who can now explore innovative soundscapes and engage with their audience in ways that transcend traditional performance boundaries. As artists experiment with these tools, they are redefining what it means to create and perform music in the modern age.
How Augmented Instruments are Changing the Music Industry
The introduction of augmented instruments is reshaping the music industry in profound ways. One of the most significant impacts is the democratization of music creation. With accessible technology, aspiring musicians can produce high-quality recordings from their homes without needing expensive studio time or extensive training.
Augmented instruments often come with user-friendly interfaces and software that simplify the music-making process, allowing individuals to experiment and develop their unique sound without barriers. Moreover, augmented instruments are fostering collaboration among artists across genres and geographical boundaries. Musicians can now connect through digital platforms, sharing their work and collaborating in real-time regardless of their physical location.
This interconnectedness has led to a surge in cross-genre experimentation, resulting in innovative musical styles that blend elements from various traditions. As artists embrace these new tools, they are not only expanding their creative horizons but also contributing to a more diverse and inclusive music landscape.
The Impact of Technology on Music Creation
| Technology | Impact on Music Creation |
|---|---|
| Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) | Allows for easy recording, editing, and mixing of music |
| Virtual Instruments | Enables musicians to access a wide range of sounds and instruments |
| Auto-Tune | Alters pitch and corrects vocal performances |
| Online Distribution Platforms | Provides opportunities for independent artists to share and sell their music |
| Streaming Services | Changes the way music is consumed and distributed |
Technology has always played a pivotal role in shaping music creation, but its influence has intensified in recent years with the rise of digital tools and platforms. The advent of digital audio workstations (DAWs) has revolutionized how music is composed, recorded, and produced. Musicians can now manipulate sound with unprecedented precision, layering tracks, applying effects, and editing recordings with ease.
This level of control allows for greater experimentation and creativity, enabling artists to push the boundaries of their craft. Additionally, technology has transformed how music is distributed and consumed. Streaming services have become the primary means through which listeners access music, fundamentally altering the traditional music business model.
Artists can now reach global audiences without relying on record labels or physical distribution channels. This shift has empowered independent musicians to carve out their niche in the industry while also challenging established norms regarding how music is marketed and monetized. As technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly shape the future of music creation in ways yet to be imagined.
The Role of Augmented Reality in Music
Augmented reality (AR) is emerging as a powerful tool in the realm of music, enhancing both performance experiences and audience engagement. By overlaying digital information onto the physical world, AR allows musicians to create immersive environments that captivate audiences in new ways. For instance, during live performances, artists can use AR to project visuals that complement their music, creating a multisensory experience that deepens emotional connections with listeners.
Moreover, AR is being utilized in music education, providing students with interactive learning experiences that enhance their understanding of musical concepts. Through AR applications, learners can visualize complex musical structures or receive real-time feedback on their playing techniques. This innovative approach not only makes learning more engaging but also caters to diverse learning styles, ensuring that students can grasp challenging concepts more effectively.
As AR technology continues to advance, its integration into music will likely expand further, offering even more opportunities for creativity and exploration.
Advantages and Challenges of Augmented Instruments
The rise of augmented instruments brings with it a host of advantages that can significantly enhance musical expression. One notable benefit is the ability to create unique sounds that blend traditional acoustic qualities with digital manipulation. Musicians can explore new sonic territories by layering sounds or applying effects that would be impossible with conventional instruments alone.
This versatility allows for greater artistic freedom and encourages experimentation across genres. However, alongside these advantages come challenges that musicians must navigate. The reliance on technology can sometimes lead to a disconnect between performers and their instruments, as musicians may become overly dependent on digital enhancements rather than honing their traditional skills.
Additionally, there is a learning curve associated with mastering augmented instruments and their accompanying software, which may deter some musicians from fully embracing these innovations. Striking a balance between technological integration and traditional musicianship will be crucial as artists continue to explore the potential of augmented instruments.
The Future of Live Performances with Augmented Instruments
The future of live performances is poised for transformation as augmented instruments become more prevalent in concert settings. Artists are beginning to experiment with interactive elements that engage audiences in unprecedented ways. For example, some performers are incorporating audience participation through mobile apps that allow fans to influence aspects of the show in real-time.
This level of interactivity creates a shared experience between artists and listeners, fostering a sense of community that enhances the overall performance. Moreover, augmented instruments enable musicians to create visually stunning shows that go beyond mere sound. By integrating visual elements such as projections or holograms into their performances, artists can craft immersive experiences that captivate audiences on multiple sensory levels.
As technology continues to advance, it is likely that live performances will evolve into multi-dimensional experiences that blur the lines between music, art, and technology.
Augmented Instruments and Music Education
In the realm of music education, augmented instruments are proving to be invaluable tools for both teachers and students. These instruments often come equipped with features that facilitate learning by providing instant feedback on performance techniques or allowing students to visualize musical concepts in real-time. This interactive approach not only makes learning more engaging but also helps students develop a deeper understanding of music theory and composition.
Furthermore, augmented instruments can cater to diverse learning styles by offering various modes of interaction. For instance, visual learners may benefit from seeing musical notation displayed alongside their playing, while auditory learners can focus on sound manipulation techniques through hands-on experimentation. By embracing these innovative tools in educational settings, instructors can create dynamic learning environments that inspire creativity and foster a lifelong love for music.
The Intersection of Art and Technology in Augmented Instruments
The intersection of art and technology is vividly illustrated through augmented instruments, which embody the creative potential inherent in this fusion. Artists are increasingly using technology not just as a tool but as an integral part of their artistic expression. By incorporating digital elements into their work, musicians are able to challenge traditional notions of what constitutes art and redefine their creative processes.
This blending of art and technology also opens up new avenues for collaboration among artists from different disciplines. Musicians can partner with visual artists or technologists to create multimedia projects that push boundaries and explore new forms of expression. As these collaborations become more common, they will likely lead to innovative works that reflect the complexities of contemporary culture while showcasing the limitless possibilities inherent in augmented instruments.
The Potential for Collaborative Music Making with Augmented Instruments
Augmented instruments have the potential to revolutionize collaborative music-making by facilitating connections between musicians across various backgrounds and locations. With digital platforms enabling real-time collaboration, artists can work together seamlessly regardless of geographical barriers. This newfound accessibility encourages diverse collaborations that blend different musical styles and cultural influences.
Moreover, augmented instruments often come equipped with features that promote improvisation and experimentation during collaborative sessions. Musicians can easily manipulate sounds or layers in real-time, allowing for spontaneous creativity that enhances group dynamics. As artists embrace these collaborative opportunities facilitated by augmented instruments, they are likely to produce innovative works that reflect a rich tapestry of influences while fostering a sense of community within the music-making process.
Ethical and Legal Considerations in the Use of Augmented Instruments
As augmented instruments gain traction within the music industry, ethical and legal considerations must be addressed to ensure fair practices among artists and creators. One significant concern revolves around intellectual property rights; as musicians increasingly incorporate digital elements into their work, questions arise regarding ownership and attribution for samples or sounds derived from existing recordings. Additionally, there is an ongoing debate about the implications of technology on authenticity in music creation.
Some argue that reliance on augmented instruments may dilute traditional musicianship or lead to homogenized soundscapes devoid of genuine expression. Striking a balance between embracing technological advancements while preserving artistic integrity will be essential as artists navigate this evolving landscape. In conclusion, augmented instruments represent a significant evolution in the world of music creation and performance.
Their integration into various aspects of the music industry—from education to live performances—highlights both the advantages they offer as well as the challenges they present. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, it will be crucial for musicians to adapt while remaining true to their artistic vision amidst this transformative era.
FAQs
What are augmented instruments?
Augmented instruments are traditional musical instruments that have been enhanced with technology to expand their capabilities and create new sounds.
How are augmented instruments different from traditional instruments?
Augmented instruments incorporate sensors, actuators, and digital interfaces to enable new modes of interaction and sound manipulation, whereas traditional instruments rely solely on acoustic or mechanical means of sound production.
What types of technology are used to augment instruments?
Technology used to augment instruments includes sensors for detecting motion and touch, actuators for creating vibrations and haptic feedback, and digital interfaces for controlling and manipulating sound in real-time.
What are some examples of augmented instruments?
Examples of augmented instruments include the ROLI Seaboard, a keyboard controller with a soft, continuous surface for expressive playing, and the Eigenharp, a versatile electronic instrument with a wide range of sensors and controls.
How are augmented instruments used in music performance and composition?
Augmented instruments allow musicians to explore new sonic possibilities, perform expressive gestures, and integrate electronic and acoustic sounds in innovative ways, expanding the creative potential of music performance and composition.